Algo trading uses a computer program that follows a defined set of instructions (an algorithm) to place a trade. The algorithm could define variables such as timing, price, volume, or any mathematical model. The computer program will automatically monitor stock prices and place buy and sell orders when defined conditions are met.
Algo orders placed with Futu include Time-Weighted Average Price (TWAP), Volume-Weighted Average Price (VWAP) and Percentage of Volume(POV) orders.
It is characterized by an algorithm that evenly splits orders over a defined time period, resulting in a consistent pace of order submission.
A TWAP order splits one large order into smaller orders based on the TWAP (Time-Weighted Average Price) Algorithm that aims to achieve an execution price close to the intraday market TWAP over a defined time period.
A VWAP order splits one large order into smaller orders based on the VWAP (Volume-Weighted Average Price) Algorithm that aims to achieve an execution price close to the intraday market VWAP over a defined time period.
It uses historical volume data to predict the trading volume for a defined time period on a given day, and splits orders proportionally to the prediction.
A POV splits a large order into smaller orders based on the POV (Percentage of Volume) Algorithm which closely tracks the market rhythm for a defined time period, and adjusts the level of participation depending on whether the market is relatively active or quiet. Its goal is to minimize market impact while still trying to achieve the desired trading volume ratio set by the user.
It is characterized by its ability to split orders based on the level of trading activity during a specified time period, and its execution efficiency is dependent on the current trading volume.
Note: The algo orders listed above may not be completely filled during the specified time period. Any unfilled orders will be cancelled after the end time has been reached.
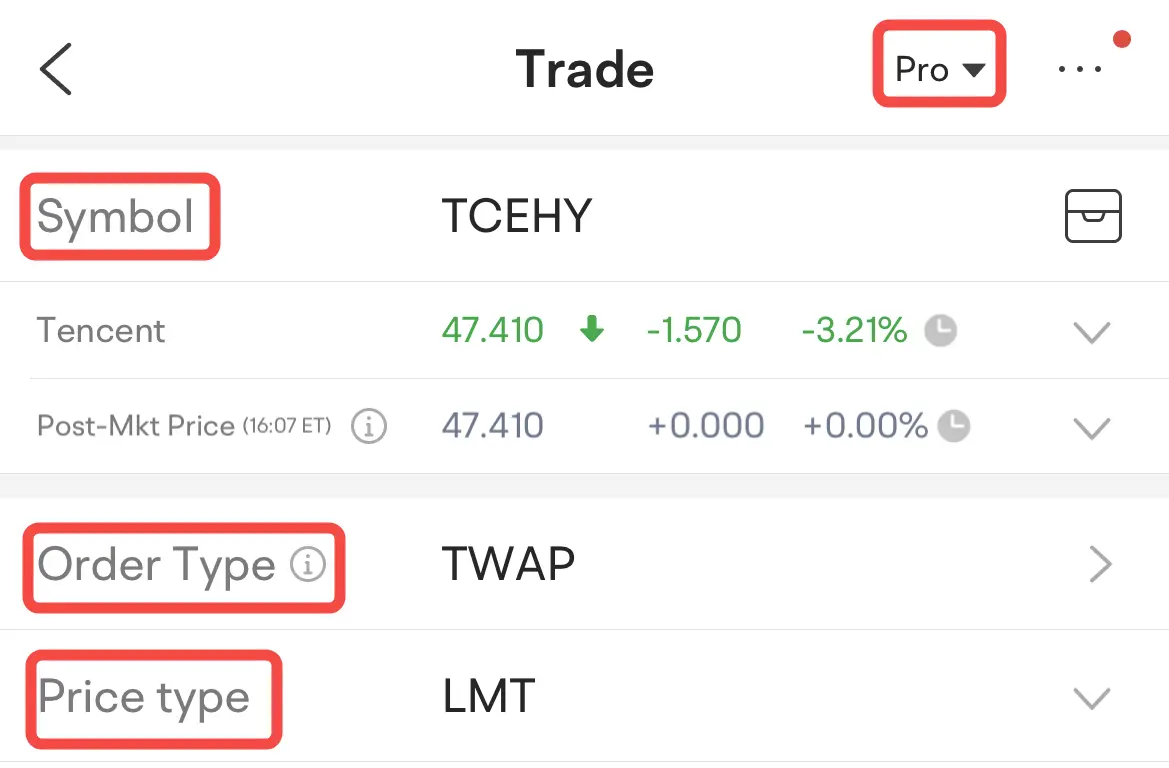
To place an algo order for US stocks, go to:
Trade page > Order Type
Find TWAP, VWAP and POV orders in the drop-down box
Set a Market (MKT) or Limit (LMT) price type
Note: If you want the order to be executed at a specific price, select LMT. If you want the order to be executed at the market price, please select MKT.
The above pictures are for illustration purposes only and do not constitute investment advice.
If you choose TWAP:
Select the price type
Enter a price (for LMT only)
Enter the quantity
Set the start time and end time for order execution
Tap Buy or Sell to submit the order.
If you choose VWAP:
Select the price type
Enter a price (for LMT only)
Enter the quantity
Set the start time and end time for execution
Enter the Max % to control the maximum order size to be filled in proportion to the predicted trading volume
Tap Buy or Sell to submit the order
If you choose POV:
Select the price type
Enter a price (for LMT only)
Enter the quantity
Set the start time and end time of execution
Enter the percentage of volume;
Tap "Buy" or "Sell", then you can successfully submit the order.
The symbols, or stocks available to trade with algo orders may be adjusted from time to time, and the details are subject to what is shown on the Trade page when placing an order.
There is no additional charge for US stocks.
There are special characteristics and risks associated with algorithmic trading. You should read the risk disclosure statement in relation to algorithmic trading before entering into any transactions. You should understand these risks and determine whether algorithmic trading is appropriate in light of your objectives and experience.
(1) Technical Errors: Algorithmic trading can be affected when your systems, the Company's systems, or the Exchanges' systems are experiencing technical difficulties. Risks include possible delays or failures in (i) the availability of your connection to the Company's services and of the Company's services to the relevant Exchange; (ii) the operation of databases and internal transfers of data; (iii) the provision of data feeds (accuracy of data and stability of data connections); (iv) possible hardware failures; (v) usage loads, bandwidth limitations, and other bottlenecks inherent in computerized and networked architectures; (vi) issues, disputes, or failures of third party vendors and other dependencies; and (vii) other general risks inherent in computer-based operations. Any of these could lead to delays or failures in order execution, incorrect order execution, and other problems.
(2) Software and Design Flaws: All software is subject to inadvertent programming errors and bugs embedded in the code comprising that software. Algo order types may contain logical errors in the code to implement them. Errors may exist in the data used for testing the algorithm or the applicable model of the market. Despite testing and monitoring, inadvertent errors and bugs may still cause algo orders to fail or run incorrectly.
(3) Market Impact and Events: Market conditions will impact the execution of algo orders. Possible adverse market conditions include a lack of liquidity, price swings, late market openings, early market closings, market chaos, mid-day trading pauses, and other disruptive events. The execution of an algorithm can itself have an impact on the market, including causing a lack of liquidity or abrupt, unwarranted price swings.
(4) Losses: Losses can happen more quickly with electronic and algorithmic trading compared to other forms of trading. Any or all of the above risk factors could cause more significant trading losses when using algorithmic trading compared to other forms of trading.

- No more -